The Adverse Effects of Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC), Unwanted Odors, and Dust on Education in Classrooms and the Role of Heat Recovery Ventilation Systems in Mitigating Them
In classrooms, air quality is of critical importance for the health, comfort, and learning performance of students. Harmful emissions such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can negatively impact indoor air quality and harm students’ education. However, heat recovery ventilation systems play a significant role in mitigating these negative effects. In this blog post, we will examine the effects of CO2, VOCs, dust, and similar pollutants in classrooms, as well as the importance of heat recovery ventilation systems in preventing these effects.
The Impact of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) and Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) on Education:
CO2 is a gas naturally produced during human respiration. In classrooms with high student density, CO2 levels can rise due to students’ respiration. VOCs are chemical substances that evaporate from paint, furniture, cleaning materials, and other sources. The adverse effects of high CO2 levels and commonly found VOCs in classrooms include:.
- Attention and Focus Issues: High CO2 levels can cause students to experience attention deficit, difficulty focusing, and cognitive performance decline, hindering their ability to focus on lessons and learn.
- Fatigue and Lethargy: Inadequately ventilated classrooms with high CO2 levels can lead to lethargy, fatigue, and low energy levels in students, negatively impacting their active participation and performance in lessons.
- Decreased Learning Performance: High CO2 levels can diminish students’ learning performance. Research indicates that poor indoor air quality in classrooms negatively affects students’ academic achievements.
- Respiratory Issues: Inhaling VOCs can lead to respiratory issues in students. Symptoms can worsen, especially in students with respiratory conditions like asthma.
- Headaches and Nausea: High VOC levels can cause headaches, nausea, and even dizziness in students, affecting their participation in lessons.
- Dermatological Issues: Some VOCs can cause skin irritation, which can be problematic for students with sensitive skin.
The Role of Heat Recovery Ventilation Systems:
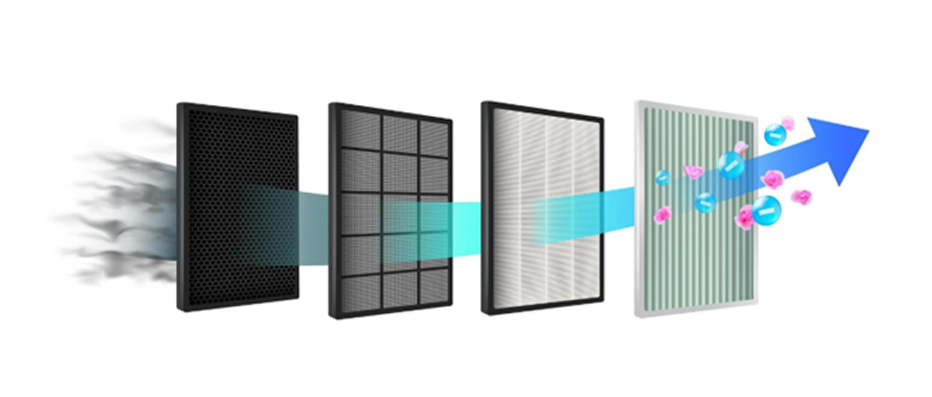
Heat recovery ventilation systems are devices that provide heat transfer between indoor and outdoor airflows. The effects of these systems in reducing levels of CO2, VOCs, dust, and similar pollutants in classrooms include:
- Air Purification: Heat recovery ventilation systems can reduce pollutants such as CO2 and VOCs by filtering the incoming air.
- Providing Fresh Air: These systems continuously provide fresh air, reducing indoor pollutant levels and ensuring students are in a cleaner environment.
- Energy Efficiency: Heat recovery ventilation systems recover the energy of the expelled air, resulting in energy savings. This enhances the sustainability of classrooms.
In conclusion, heat recovery ventilation systems enable students to access the fresh air they need for a healthy education, remove unwanted pollutants and odors from the educational environment, and improve energy efficiency.
Thank you for following along.







